Intralytix, Inc.
is focused on the discovery, production and marketing of bacteriophage-based products to control bacterial pathogens in environmental, food processing, and medical settings.
Products
Frequently Asked
To purchase our bacteriophage products, please contact our sales team at sales@intralytix.com. Our team will be happy to provide more information and assist you with placing an order.
Our bacteriophage products are manufactured right here in the USA. We take pride in producing high-quality, safe, and effective phage-based solutions.
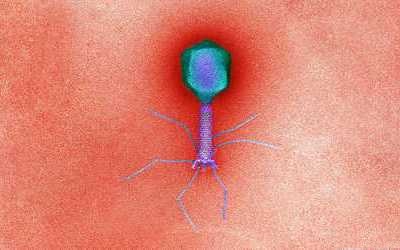
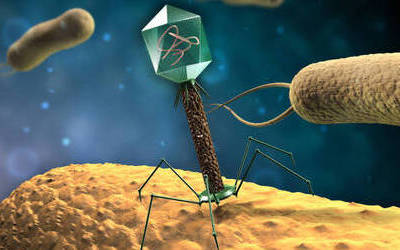
Bacteriophages are the natural predator of bacteria. They are composed of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat, and are specific to certain bacterial types.
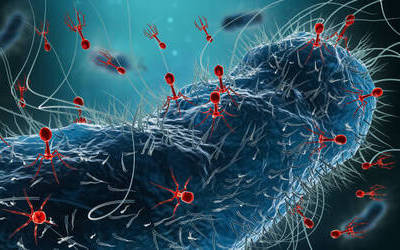
Bacteriophages attach to bacterial cells, inject their genetic material, and hijack the cell's machinery to replicate themselves, eventually causing the cell to burst and release new phages.
No, bacteriophages are non-pathogenic to humans as they only target bacterial cells, making them a safe therapeutic option.
Bacteriophages can be used in food processing and environmental applications to control bacterial contamination. See our human therapeutics page for information regarding phage therapy to treat bacterial infections.